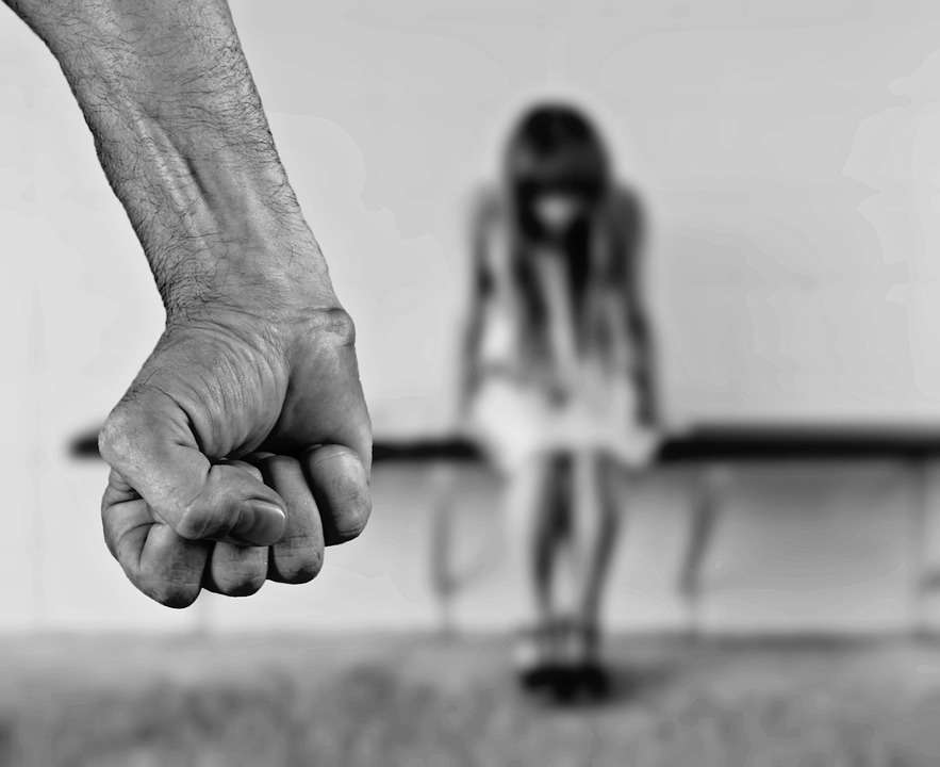
Domestic Violence: A Silent Epidemic
Domestic violence, also known as intimate partner violence, is a pattern of behaviour that involves the use of physical, emotional, or sexual abuse to gain power and control over another person in a close relationship. This can occur in any intimate relationship, including marriage, cohabitation, or dating, and affects people of all ages, genders, sexual orientations, races, ethnicities, and socio-economic backgrounds. Despite being a widespread problem, domestic violence remains a largely hidden and stigmatised issue, with victims often suffering in silence and perpetrators going unpunished. In this blog, we will explore the prevalence, causes, and consequences of domestic violence and discuss strategies for prevention and intervention.
Prevalence
Domestic violence is a global phenomenon that affects millions of people each year. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), approximately one in three women worldwide has experienced physical or sexual violence from an intimate partner at some point in their lives. In the United States, an estimated one in four women and one in nine men have experienced severe physical violence, sexual violence, or stalking by an intimate partner in their lifetime. Domestic violence also has serious economic consequences, including lost productivity, increased healthcare costs, and reduced quality of life.
Domestic violence is a broad term that includes different types of abuse. Here are the subcategories of domestic violence:


- Physical Abuse:
Physical abuse is the most visible form of domestic violence. It involves the use of physical force to harm or injure another person, and it can include hitting, kicking, punching, slapping, pushing, and choking. Physical abuse can cause serious injuries, including broken bones, bruises, cuts, and internal injuries, and it can even result in death.
2. Sexual Abuse:
Sexual abuse is another form of domestic violence that involves any unwanted sexual contact or activity. This can include rape, sexual assault, unwanted sexual touching, and forcing someone to engage in sexual activity against their will. Sexual abuse can cause physical and emotional trauma, and it can also lead to sexually transmitted infections, unwanted pregnancies, and other health problems.
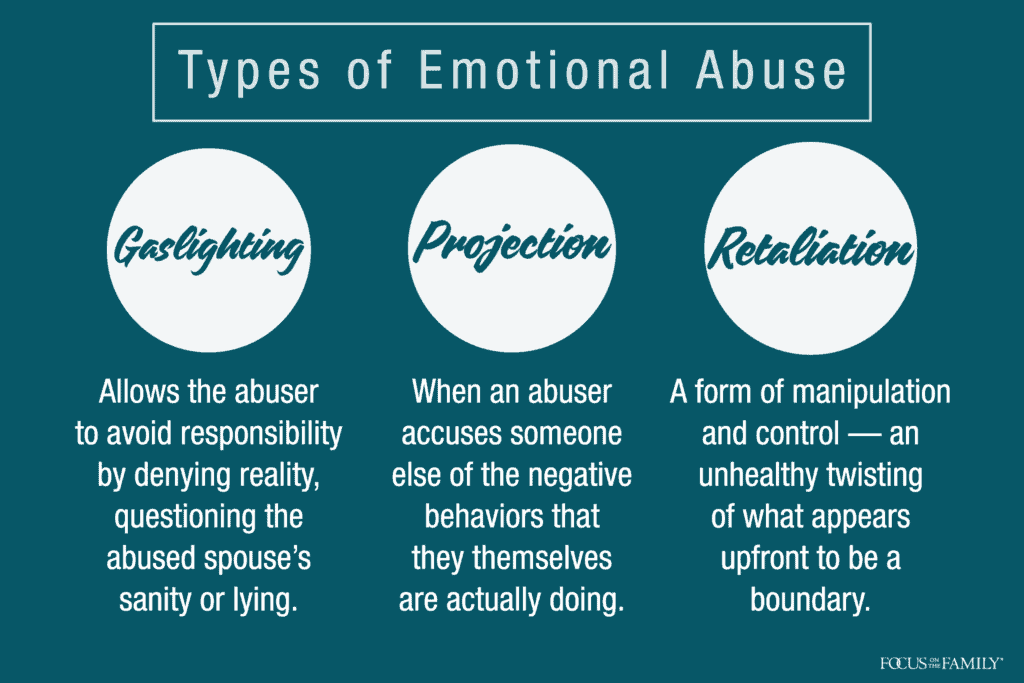

3. Emotional Abuse:
Emotional abuse is another form of domestic violence that is less visible but can be just as damaging as physical abuse. Emotional abuse involves the use of words, actions, or threats to control, manipulate, or intimidate another person. This can include insults, put-downs, threats, isolation, and humiliation. Emotional abuse can cause long-lasting emotional and psychological damage, including anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.


4. Psychological abuse:
This type of abuse involves causing fear or distress through threats, intimidation, or other non-physical means. It includes gaslighting, stalking, blackmail, and using children as leverage.


5. Financial Abuse:
Financial abuse is a form of domestic violence that involves controlling or manipulating someone’s finances. This can include stealing money, preventing someone from working or attending school, and controlling someone’s access to money or credit. Financial abuse can leave victims financially vulnerable and can make it difficult for them to leave an abusive relationship.
Causes of Domestic Violence
Domestic violence is a complex issue that is caused by a variety of factors. Some of the common causes of domestic violence include:
- Power and Control: Domestic violence is often about power and control. The abuser wants to have power and control over their partner, and they use violence as a way to maintain that power.
- Learned Behaviour: Domestic violence is often a learned behaviour. Children who grow up in violent homes are more likely to become abusers or victims of abuse as adults.
- Mental Illness: Some abusers have mental health issues that contribute to their abusive behaviour. Mental illness can make it difficult for abusers to control their emotions and actions.
- Substance Abuse: Substance abuse can also contribute to domestic violence. Alcohol and drugs can lower inhibitions and make it easier for abusers to become violent.
- Cultural and Social Factors: Domestic violence is also influenced by cultural and social factors. Some cultures may condone or even encourage violence against women, while others may stigmatise mental health issues or substance abuse.
Effects & Signs of domestic violence
Domestic violence can have serious physical and emotional effects on victims. Some of the common effects of domestic violence include:
- Physical Injuries: Victims of domestic violence may suffer from physical injuries such as bruises, cuts, broken bones, and internal injuries.
- Emotional Trauma: Domestic violence can also cause emotional trauma, including anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and suicidal thoughts.
- Financial Problems: Abusers may use financial abuse as a way to control their victims. This can leave victims with financial problems and make it difficult for them to leave the abusive relationship.
- Social Isolation: Abusers may isolate their victims from friends and family, leaving them feeling alone and unsupported.
- Inter-generational Effects: Children who witness domestic violence may suffer from emotional trauma and have a higher risk of becoming abusers or victims of abuse as adults.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these signs, it’s important to seek help immediately.
Ways to Prevent Domestic Violence
Preventing domestic violence requires a multi-faceted approach that involves education, awareness, and intervention. Some of the ways to prevent domestic violence include:
- Education and Awareness: Educating people about the causes and effects of domestic violence can help to raise awareness and prevent it from happening in the first place.
- Early Intervention: Early intervention can help to prevent domestic violence from escalating. This can include counseling and support for victims, as well as anger management and other forms of therapy for abusers.
- Support for Victims: Victims of domestic violence need support and resources to help them leave abusive relationships and rebuild their lives. This can include safe housing, financial assistance, and counseling.
- Legal Intervention: The legal system can also play a role in preventing domestic violence. Laws that criminalize domestic violence can provide victims with legal protection and hold abusers accountable for their actions.
- Community Support: Communities can also play a role in preventing domestic violence. This can include creating support groups for victims, providing education and resources, and promoting healthy relationships.
Where to get help
If you or someone you know is experiencing domestic violence, there are many resources available to help. Some of the places you can turn to for help include:
- National Domestic Violence Hotline: Call 1-800-799-SAFE (7233) for free and confidential help 24/7.
- Local domestic violence shelters: Find a shelter near you contacting the National Domestic Violence Hotline or searching online.
- Law enforcement: If you are in immediate danger, call 911 or your local police department.
- Medical professionals: Talk to your doctor or nurse, who can connect you with resources and support.
- Family and friends: Reach out to people you trust for support and help.

Creating a safety plan
If you or someone you know is experiencing domestic violence, it’s important to create a safety plan to help reduce the risk of harm. A safety plan should include:
- A list of emergency phone numbers, including the National Domestic Violence Hotline, local domestic violence shelters, and law enforcement.
- A safe place to go in case of an emergency, such as a friend’s house or a domestic violence shelter.
- A code word or signal to alert family and friends that you need help.
- A plan for how to leave the situation safely, including where to go and what to bring.
Domestic violence is a significant problem in India, and it affects women, children, and men. According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), there were over 4.05 lakh cases of cruelty by husbands or their relatives reported in 2019. The actual number of cases is likely to be much higher as many cases go unreported due to social stigma, fear, and lack of support. Women are the primary victims of domestic violence in India, and they suffer from physical, sexual, emotional, and economic abuse.
Remember, domestic violence is never your fault. There is help available, and you are not alone. If you or someone you know is experiencing domestic violence, reach out for help as soon as possible.
FOLLOW US ON @MAHILAWORLD100 FOR MORE SUCH CONTENT.